ВхюЖи╝ВЌљвіћ ьЋўВѕўВ▓ўвдгВЮў ВІаЖИ░Вѕа ВцЉ ьЋўвѓўвАю вДЅвХёвдг ЖИ░ВѕаВЮ┤ вёљвдг ВЌ░Жхг в░Ј ВаЂВџЕвљўЖ│а ВъѕвІц. ВцЉваЦ вХёвдг, ВЮЉЖ│а, ВюаВаю вХёьЋ┤, ВўцВЮ╝ ьЮАВѕў в░Ј Віцьѓцв░Ї, ВЃЮвХёьЋ┤, ВЮЉВДЉ ьЮАВ░Е, ВЮ┤Вўе ЖхљьЎў в░Ј ЖИ░ьЃђ ЖИ░ВА┤ вХёвдг Ж│хВаЋЖ│╝ Ж░ЎВЮђ вІцвЦИ ЖИ░ВѕаЖ│╝ в╣ёЖхљьЋа вЋї ВЮ┤ ЖИ░ВѕаВЮђ вДјВЮђ ВъЦВаљВЮё Ж░ђВДђЖ│а ВъѕВіхвІѕвІц. Ж░ЋваЦьЋю ВёаьЃЮВё▒, вѓ«ВЮђ ВЌљвёѕВДђ Вєїв╣ё, вёЊВЮђ ВаЂВџЕ в▓ћВюё, ьЎўЖ▓й В╣юьЎћВаЂВЮ┤Ж│а Ж░ёвІеьЋю ВъЦв╣ё, ВЅгВџ┤ ВъЉвЈЎ вЊ▒. ВюаВѕўвХёвдгвДЅВЮђ ВъгВДѕВЌљ вћ░вЮ╝ ВюаЖИ░вДЅЖ│╝ вг┤ЖИ░вДЅВю╝вАю ЖхгвХёвљЕвІѕвІц. ВюаЖИ░вДЅВЮђ Ж│╝ьЋЎ ВЌ░Жхг в░Ј ВЃЂВЌЁ вХёВЋ╝ВЌљВёю ьЈГвёЊЖ▓ї ВЮЉВџЕвљўЖ│а ВъѕВіхвІѕвІц. ВюаЖИ░вДЅВЌљ в╣ёьЋ┤ вг┤ЖИ░ ВёИвЮ╝в»╣вДЅВЮђ ьЎћьЋЎВаЂ, ВЌ┤ВаЂ ВЋѕВаЋВё▒ВЮ┤ Ж░ЋьЋўЖ│а вѓ┤ВўцВЌ╝Вё▒ в░Ј вѓ┤ВЋЋВё▒ВЮ┤ Вџ░ВѕўьЋўвЕ░ ВёИВ▓ЎВЮ┤ ВџЕВЮ┤ьЋўЖ│а ЖИ░Ж│ёВаЂ Ж░ЋвЈёЖ░ђ вєњВю╝вЕ░ ВѕўвфЁВЮ┤ ЖИИЖИ░ вЋївгИВЌљ ВѕўВцЉВюа ВЌљвЕђВа╝ вХёвдгВЌљ ВёИвЮ╝в»╣вДЅВЮё ВѓгВџЕьЋўвіћ Ж▓ЃВЮ┤ ВцЉВџћьЋЕвІѕвІц. Ж▓йьќЦ. ВєїВѕўВё▒ Ж░юВДѕВЮђ ВёИвЮ╝в»╣ ьЋёвдёВЮў ВўцВЮ╝ ВіхВюцВё▒ВЮё ьќЦВЃЂВІюьѓцЖ│а, ВюаВцЉВѕў ВЌљвЕђВа╝ВЮў вХёвдг ьџеВюеВЮё ьќЦВЃЂВІюьѓцвЕ░, ВёИвЮ╝в»╣ ьЋёвдёВЮў ьЎћьЋЎВаЂ ВЋѕВаЋВё▒Ж│╝ вѓ┤ЖхгВё▒ВЮё ьќЦВЃЂВІюьѓг Вѕў ВъѕВіхвІѕвІц.
ВюаВцЉВѕў(W/O) ВЌљвЕђВа╝ ВІюВіцьЁюВЮў ьўЋьЃювіћ вг╝ВЮ┤ ВъЉВЮђ вг╝в░ЕВџИ ьўЋьЃювАю ВўцВЮ╝ВЌљ вХёВѓ░вљўвіћ Ж▓ЃВъЁвІѕвІц. вДЅвХёвдг ВІю вДЅВўцВЌ╝ВЮђ ВѓгВџЕВІюЖ░ёВЮў ВЌ░ВъЦВЌљ вћ░вЮ╝ ьѕгЖ│╝ВюаВєЇ в░Ј ВюаВДђВюеВЮў Ж░љВєївАю ВЮ┤Вќ┤ВаИ вДЅВЮў ВѕўвфЁВЮё вІеВХЋВІюьѓцЖ│а вДЅвХёвдг ЖИ░ВѕаВЮў ВаЂВџЕВЮё ВаюьЋюьЋювІц. ВёИвЮ╝в»╣ вДЅ ьЉювЕ┤ВЮў в│ђьўЋВЮђ вДЅВЮў ьі╣ВаЋ ВёаьЃЮВё▒Ж│╝ вХёвдг ьџеЖ│╝вЦ╝ ьќЦВЃЂВІюьѓцЖ│а вДЅ ьЉювЕ┤Ж│╝ вХѕьЋёВџћьЋю Ж│хЖИЅ вХёВъљ Ж░ёВЮў ВЃЂьўИ ВъЉВџЕВЮё ВцёВЮ┤вЕ░ вДЅ ВўцВЌ╝ВЮё Вќ┤віљ ВаЋвЈё ВцёВЮ╝ Вѕў ВъѕВіхвІѕвІц. вћ░вЮ╝Вёю ВюаВцЉВѕў ВЌљвЕђВа╝ВЮў вХёвдгвіћ ВЮ╝в░ўВаЂВю╝вАю ВєїВѕўВё▒ ьЋёвдёВЮё ВёаьЃЮьЋўВЌг вДЅ ьЉювЕ┤ВЮў ВєїВѕўВё▒Ж│╝ В╣юВюаВё▒ ьі╣Вё▒ВЮё ВЮ┤ВџЕьЋўВЌг ЖИ░вдё в░ЕВџИВЮ┤ ьєхЖ│╝ьЋўЖ│а вг╝в░ЕВџИВЮё Ж░ђвЉљВќ┤ ВюаВѕў ьџеЖ│╝вЦ╝ Вќ╗ВЮё Вѕў ВъѕвЈёвАЮ ьЋЕвІѕвІц. вХёвдг.
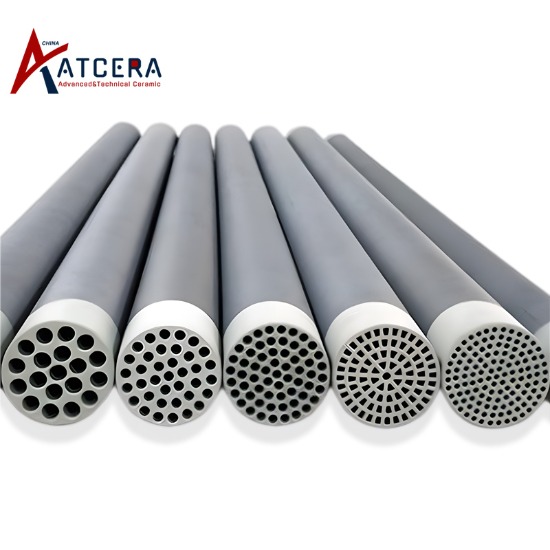

ВёИвЮ╝в»╣ вДЅ ьЉювЕ┤ВЮў ВєїВѕўВё▒ Ж░юВДѕ
ВёИвЮ╝в»╣ ьЋёвдё ьЉювЕ┤ВЮў ВєїВѕўВё▒ Ж░юВДѕВЮђ ВЮ╝в░ўВаЂВю╝вАю ВєїВѕўВё▒ вг╝ВДѕВЮё Ж▓░ьЋЕьЋўЖ▒░вѓў ВаЉВ░ЕьЋўЖ│а, ьЉювЕ┤ ьЎћьЋЎВаЂ ьі╣Вё▒ВЮё ВаюЖ│хьЋўЖИ░ ВюёьЋ┤ ВІцвъђВЮ┤вѓў ьІ░ВўгВЮё ВѓгВџЕьЋўвіћ Ж▓ЃЖ│╝ Ж░ЎВЮ┤ вЇћ вѓ«ВЮђ ьЉювЕ┤ ВЌљвёѕВДђ, ВаЂВаѕьЋю Ж▒░В╣аЖИ░ в░Ј ьЉювЕ┤ ЖхгВА░вЦ╝ ВёаьЃЮьЋўЖ│а, ВёИвЮ╝в»╣ ьЋёвдё ьЉювЕ┤ВЌљ вДѕВЮ┤ьЂгвАа вўљвіћ вѓўвЁИ ЖхгВА░вЦ╝ вЈёВъЁьЋеВю╝вАюВЇе вІгВё▒вљЕвІѕвІц. вЇћ вѓўВЮђ Ж▒░В╣аЖИ░вЦ╝ Ж░ђВДё ьЉювЕ┤ВЮё Вќ╗Ж│а, ьЋёвдё ьЉювЕ┤ВЮў ВєїВѕўВё▒ ьџеЖ│╝вЦ╝ ьќЦВЃЂВІюьѓцвЕ░, вХёвдг Вё▒віЦВЮё ьќЦВЃЂВІюьѓхвІѕвІц.
ВёИвЮ╝в»╣ вДЅ ьЉювЕ┤ВЮў ВєїВѕўВё▒ Ж░юВДѕВЌљвіћ ьЋеВ╣е, ВАИ-Ж▓ћ, ьЎћьЋЎ ЖИ░ВЃЂ ВдЮВ░ЕВЮў ВёИ Ж░ђВДђ ВЮ╝в░ўВаЂВЮИ в░Ев▓ЋВЮ┤ ВъѕВіхвІѕвІц.
01. вћЦ в░ЕВІЮ
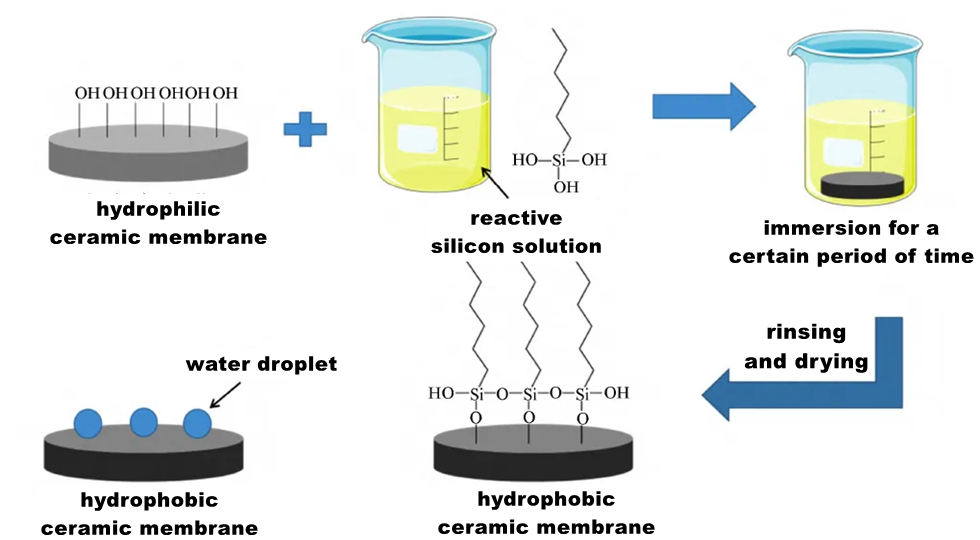
Impregnation method (Impregnation method) does not require special equipment, just the original ceramic film directly immersed in hydrophobic substance solution, the method is simple and direct, easy to operate, low cost. The hydrophobic modification of ceramic membrane surface is carried out by immersion method, which usually uses the functional group of hydrophobic substance to connect with the hydroxyl group on the ceramic membrane surface through condensation reaction.
Taking siloxane as a modifier for example, the operation steps of the impregnation method are as follows: dissolve the organosilane in water or ethanol and hydrolyze it to obtain a reactive silanol solution; When the pre-treated ceramic membrane is immersed in the solution, the reactive silane molecules can be adsorbed on the surface of the membrane, and the hydrophobic membrane can be obtained.
Hydrophobic effect is the result of the joint action of surface roughness and surface energy. In the study of hydrophobic modification of ceramic film, it is usually first to provide a certain rough micro-nano structure on the surface of ceramic film, and then modify it with low surface energy. In addition to the modification with silane coupling agent, mercaptan is also the preferred material to reduce the surface energy of the film.
In summary, the operation and steps of hydrophobic modification of the surface of ceramic film by impregnation method are relatively simple, and are greatly affected by the type of modifier, the concentration of modifier, the impregnation time, the number of impregnation times and the roughness of the surface of ceramic film. In addition, because the number of substances with low surface energy that react depends on its own concentration and the number of hydroxyl groups on the surface of ceramic film, Therefore, the method also has a great dependence on the reactive hydroxyl group on the surface of the ceramic membrane.
02. Sol-gel method
Sol-gel technique uses compounds containing highly chemically active components as precursors, and mixes these raw materials uniformly in the liquid phase. After chemical reactions such as hydrolysis and condensation, a stable transparent Sol system is formed in the solution. The sol is slowly polymerized among aged colloidal particles to form a gel with a three-dimensional network structure. The gel was dried and sintered to produce molecular and even nanostructured materials.
The hydrophobic modification of ceramic membrane by sol-gel method can form a large rough structure on the surface of the membrane, and can directly bind low surface energy chemicals. However, the early introduction of organosilane into the sol solution may lead to the formation of large volume polymers, resulting in poor modification effects.
Compared with other methods, sol-gel method can prepare a stable hydrophobic surface with good separation effect, but it takes a long time to prepare the sol solution, and macromolecular polymers may be formed in the process, which affects the modification effect. In general, secondary sintering is required after the completion of coating, and the process is more complicated. In addition, excessive temperature during secondary sintering will destroy the structure of the film, reduce the hydrophobicity and stability of the film, and the aperture of the modified film will decrease with the increase of the number and time of sol-gel coating. In addition, the sol has an important effect on the formation of colloid in the process of colloid preparation, and then affects the film forming quality. Coating time and times, ambient temperature and humidity, heating rate, calcination temperature and calcination time all have a great influence on the subsequent coating drying process. At present, the process can be simplified by reducing the sintering steps at high temperature, forming a rough structure on the surface of the film at one time and combining with low surface energy materials, so as to reduce the damage of the film structure at high temperature.

03 Chemical vapor deposition method
chemical vapor deposition (CVD) uses gas phase reactants deposited on the substrate surface to form a solid film with specific chemical properties. The method has the advantages of controllable film composition, good film repeatability, uniform film layer, wide application range, no restriction on the shape of the substrate and no damage to the substrate material, and is an effective method to change the surface properties and microstructure of the film. For hydrophobic modification of the ceramic film using this method, the ceramic film needs to be placed in a closed container and heated at the boiling point temperature of the organosilane for a long time. The organosilane vapor is passed through to react with the hydroxyl group on the surface of the ceramic film, and the reaction principle is the same as that of the impregnation method.
Under normal circumstances, in order to make the organosilane reagent can be fully utilized, it is necessary to select a closed container with a size similar to the ceramic membrane, so that the contact and reaction of organosilane vapor with the ceramic membrane can be maximized.
CVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition)віћ ьЋёвдё ьЉювЕ┤ВЌљ вДѕВЮ┤ьЂгвАювѓўвЁИВъЁВъљВЎђ вѓўвЁИвДЅвїђвЦ╝ Вцђв╣ёьЋўЖ│а ЖиюВ╣ЎВаЂВЮИ в»ИВёИЖхгВА░вЦ╝ ьўЋВё▒ьЋўвіћ вЇ░ ВёаьўИвљўвіћ в░Ев▓ЋВЮ┤вІц. ьЎћьЋЎЖИ░ВЃЂВдЮВ░Ев▓ЋВю╝вАю Ж░юВДѕвљю ВєїВѕўВё▒ ВёИвЮ╝в»╣ ьЋёвдёВЮђ ьЋёвдёВИхВЮ┤ ЖиаВЮ╝ьЋўЖ│а ВЋѕВаЋВё▒ВЮ┤ ВбІВю╝вЕ░ ВаЂВџЕ в▓ћВюёЖ░ђ вёЊвІцвіћ ВъЦВаљВЮ┤ ВъѕВю╝вѓў, вЈЎВІюВЌљ ВєїВѕўВё▒ ьЋёвдёВЮў вЉљЖ╗ўЖ░ђ ВќЄВЋё ЖИ░Ж│ёВаЂ вг╝Вё▒ВЮ┤ вХђВА▒ьЋўЖ│а ьЂгвъЎ, ЖиаВЌ┤ вЊ▒ВЮў Ж▓░ьЋеВЮ┤ в░юВЃЮьЋўвіћ вгИВаюВаљВЮ┤ ВъѕвІц. ВЎИвХђ ВХЕЖ▓ЕВЌљ ВЮўьЋ┤ ЖИ░ьЈгЖ░ђ в░юВЃЮьЋўЖИ░ ВЅйВіхвІѕвІц. ьЋёвдёВЮў ЖиаВЌ┤ВЮё ьєхьЋ┤ вг╝в░ЕВџИЖ│╝ ВўцВЌ╝вг╝ВДѕВЮ┤ В╣еьѕгьЋўВЌг вѓ┤вХђ ЖхгВА░вЦ╝ ьїїЖ┤┤ьЋўЖ│а, ьЋёвдёВЮў ВєїВѕўВё▒Ж│╝ ВЋѕВаЋВё▒ВЮё ВађьЋўВІюьѓхвІѕвІц. ВдЮВ░Е в░ўВЮЉВЌљ Ж┤ђВЌгьЋўвіћ ВЮ╝вХђ ВюаЖИ░ВІцвъђВЮђ вЈЁВё▒ВЮ┤ ВъѕВќ┤ ВЮИВ▓┤ВЎђ ьЎўЖ▓йВЌљ ьЋ┤вЦ╝ вЂ╝В╣а Вѕў ВъѕВіхвІѕвІц. вўљьЋю, ВЮ┤ в░Ев▓ЋВЌљ ьЋёВџћьЋю в░ўВЮЉ ВўевЈёЖ░ђ вєњЖ│а ЖиИВЌљ вћ░вЦИ вєњВЮђ ВЌљвёѕВДђ Вєїв╣ёВЎђ вєњВЮђ в╣ёВџЕВю╝вАю ВЮИьЋ┤ ВІцВаю Вѓ░ВЌЁ ВЃЮВѓ░ВЌљ ВаЂВџЕьЋўвіћ вЇ░ ВаюьЋюВЮ┤ ВъѕВіхвІѕвІц.





























