현재 SiC와 GaN으로 대표되는 3세대 반도체의 출현으로 파워 모듈은 소형화, 고전압, 고전류, 고전력 밀도 방향으로 발전하고 있으며, 이는 사용 중에 더 높은 열을 발생시킬 것입니다. 장치의 방열 패키지에 대한 엄격한 요구 사항. 차세대 고전력 모듈에서 세라믹 기판은 주로 칩 지지, 전기 절연 및 열 전도성 채널 역할을 하며, 질화규소 세라믹은 높은 열 특성으로 인해 응용 잠재력이 큰 방열 기판 재료가 되었습니다. 전도성과 높은 기계적 성질.
기계적 특성과 열 전도성을 모두 갖춘 고성능 질화규소 기판을 얻는 방법은 오늘날 업계에서 가장 우려되는 문제 중 하나입니다. 질화 규소 세라믹 기판의 Si 및 N 원자의 확산 계수가 낮기 때문에 액상 소결을 통해 상 변형, 결정립 발달 및 치밀화가 달성되어야 합니다. 따라서 적절한 소결 첨가제를 사용하여 소결 공정에서 액상 및 미세 형태를 조정하는 것은 질화 규소 세라믹의 기계적 및 열적 특성을 향상시키는 효과적인 방법입니다.
비산화물 소결 AIDS의 종류
불화
규산염 용액에서 불소 원자는 규산염 네트워크의 구조를 파괴하고 분해하여 액상 형성의 온도와 점도를 낮추고 소결 치밀화를 촉진할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 소결제로 MgO 대신 MgF2를 사용하면 낮은 온도에서 액상을 형성할 수 있고, 세라믹의 치밀화를 촉진할 수 있으며, MgF2 첨가 증가에 따라 결정립 크기가 증가하여 세라믹의 열전도도를 효과적으로 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 질화 규소 세라믹. 그 밖에도 LiF, 희토류 불화물, 이원 불화물 등이 있습니다.
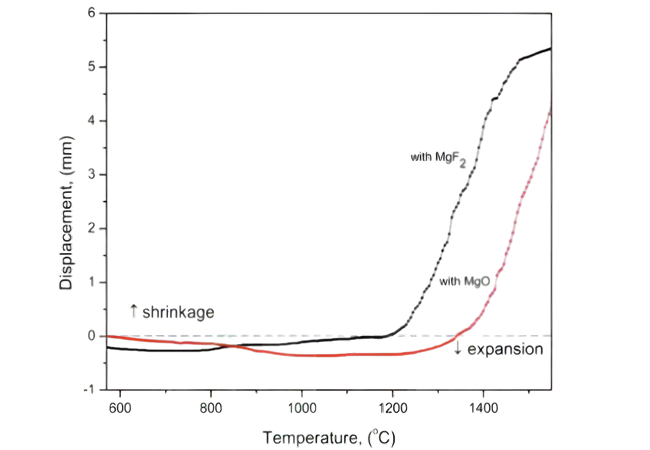
Si3N4 세라믹의 변위-온도 곡선은 MgF2와 MgO를 소결 첨가제로 사용하여 작성되었습니다.
불화물 소결 첨가제는 시스템에 산소 원자가 추가로 유입되는 것을 방지하고, 액상에서 SiO2의 활성을 감소시키며, 용해 침전 과정에서 격자 산소의 형성을 방해합니다. 동시에 불소원자에너지는 액상의 점도를 감소시키고, 저온에서 액상의 형성을 돕고, 큰 크기의 β-Si3N4 입자의 발달을 촉진하며, 제조된 질화규소 세라믹은 격자 산소량이 낮고, 열 전도성 결정간 상 함량 및 세라믹의 높은 열 전도성. 그러나 SiF4의 과도한 휘발은 세라믹의 기공률을 증가시키고 기계적 성질과 열전도도를 감소시키므로 적절한 첨가량 조절이 필요하다.
질화물 및 질소 함유 화합물
Metal nitride has good compatibility with silicon nitride ceramics, and is often used as a sintering assistant to prepare silicon nitride ceramic materials, which can enhance the thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramics and strengthen its mechanical properties. MgSiN2, as a potential high thermal conductivity ceramic, has attracted much attention as a sintering aid for silicon nitride ceramics in recent years. At high temperature, SiO2 on the surface of MgSiN2 and Si3N4 powder will form Mg-Si-O-N liquid phase and promote densification. In addition, a portion of Si and N atoms are separated out in the form of Si3N4 to optimize grain boundaries. In recent years, by using MgSiN2 instead of MgO, researchers have prepared silicon nitride ceramics with high thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical properties at lower sintering temperature and shorter holding time. Li Jiangtao's team from the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences prepared MgSiN2 in batches through self-propagating sintering, laying a material foundation for the large-scale application of MgSiN2. It is expected to be used as an efficient sintering aid for silicon nitride ceramics with high thermal conductivity.
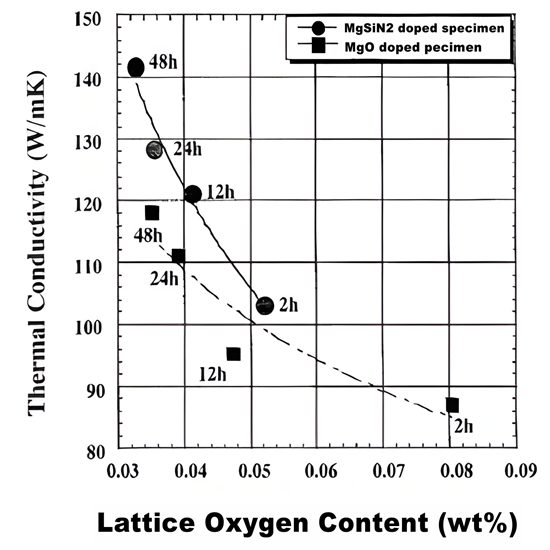
The silicon nitride ceramics with low lattice oxygen content and high thermal conductivity were prepared by using MgSiN2 as sintering assistant
In addition, some researchers used solid phase reaction to synthesize a new non-oxide sintering agent Y2Si4N6C to replace Y2O3 as a sintering agent, which not only has low lattice oxygen content, but also weakened the scattering of phonons by intergranular phase and grain boundary film, which can greatly improve the thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramic substrate. However, the preparation process of Y2Si4N6C is complex, and it cannot be synthesized in large quantities for the time being, which limits its application.
Borides
The densified Si3N4 ceramics with LaB6 as the sintering agent do not introduce additional oxygen into the system, and can remove lattice oxygen through the dissolution precipitation process, improve the thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 grains, and at the same time, the content of low thermal conductivity intercrystalline phases is less, the grain size is larger, and the phonon scattering between grains is weakened. This is because during the sintering process, B atoms enter the glass network, and the formed [BO3]- structural unit will replace the [SiO4]- structural unit in the original network, destroying the integrity of the glass network, reducing the liquid phase viscosity, and thus promoting low temperature sintering.
Silicides
It has been found that iron silicide (FeSix) has a certain regulatory effect on the phase transition and grain growth of silicon nitride ceramics. For example, FeSi2 can generate β-Si3N4 phase before the α-Si3N4 phase transition, providing nucleation and growth points for the later α-Si3N4 phase transition. It is helpful to regulate the phase transition and grain growth process in the sintering of silicon nitride ceramics. ZrSi2 can react with SiO2 on the surface of silicon nitride powder to produce ZrO2 and β-Si3N4 crystal seeds. In situ ZrO2 and MgO assistant form a low temperature eutectic liquid phase, which promotes ceramic densification and β-Si3N4 grain development through dissolution precipitation mechanism. Due to the consumption of SiO2 by ZrSi2, the oxygen content in the liquid phase is reduced, thereby impeding the generation of lattice oxygen dynamically and reducing lattice defects. In addition, Zr elements in the sintered body are precipitated in the form of ZrN (or ZrO2) phase, and there is no obvious amorphous grain boundary film between Si3N4 grains, which reduces the scattering of phonons at the grain boundaries. Thanks to the above three factors, the thermal conductivity of Si3N4 has been greatly improved. However, the difficulty of both thermal conductivity and mechanical properties limits the application of ZrSi2 as a sintering aid for high-conductivity silicon nitride ceramics.
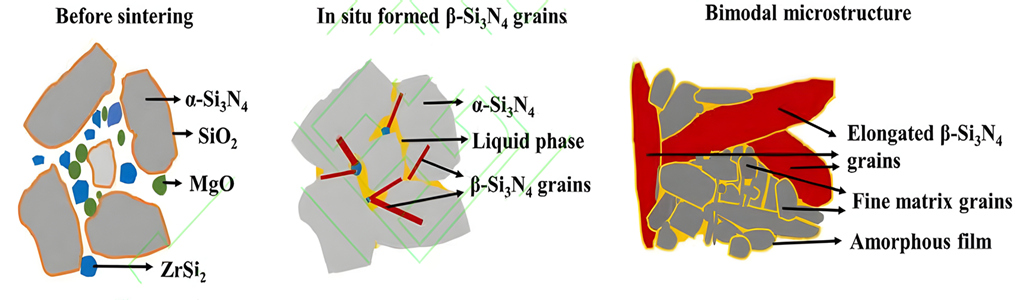
Schematic diagram of densification mechanism of silicon nitride ceramics containing ZrSi2-MgO additive
Hydrides and Metal Particles
Metal hydride is a commonly used oxygen consumption agent in powder metallurgy industry, which is decomposed into metal elements and H2 at high temperatures, H2 can remove the oxide layer on the surface of metal particles, and the highly active metal elements generated by decomposition play the role of absorbing impurity oxygen in the metal matrix, which can effectively improve the performance of metal products. Rare earth hydrides such as YH2 can reduce the activity of SiO2 in the liquid phase and facilitate the removal of lattice oxygen during dissolution precipitation. In addition, the "nitrogen-rich" liquid phase formed by the addition of YH2 is also conducive to the nucleation and development of β-Si3N4, and the grain size is significantly larger than that of Y2O3 additive system. However, excessive hydride makes the liquid viscosity too high, inhibits the densification process, and the fully developed β-Si3N4 grains cross to form a porous skeleton, which can not prepare high density silicon nitride ceramics. Therefore, it is still necessary to determine the optimal amount of rare earth hydride according to the oxygen content of α-Si3N4 raw material powder.
Ternary Layered Compound
The fracture toughness can be improved by introducing layered compounds into silicon nitride ceramic matrix through crack deflection, bridge and other mechanisms. In recent years, researchers have investigated the effect of layered compounds on the thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramics, and found that layered compounds can effectively improve the mechanical thermal properties of ceramics. YB2C2 can react with SiO2 on the surface of silicon nitride powder to reduce the liquid phase oxygen content and promote densification. The remaining YB2C2 layer improves the bending strength and fracture toughness of the ceramics through crack deflection mechanism.
Carbon, Silicon Sintering Additives
Carbon is widely used to remove oxygen impurities from ores because of its strong reducibility. In the study of silicon nitride, a small amount of carbon can promote α→β phase transition in silicon nitride sintering. Carbon thermal reduction deoxygenation can adjust the composition and properties of the liquid phase, and then regulate the relative rate of phase transition and densification, so that the silicon nitride ceramics with good morphology can be obtained without adding β-Si3N4 seed.
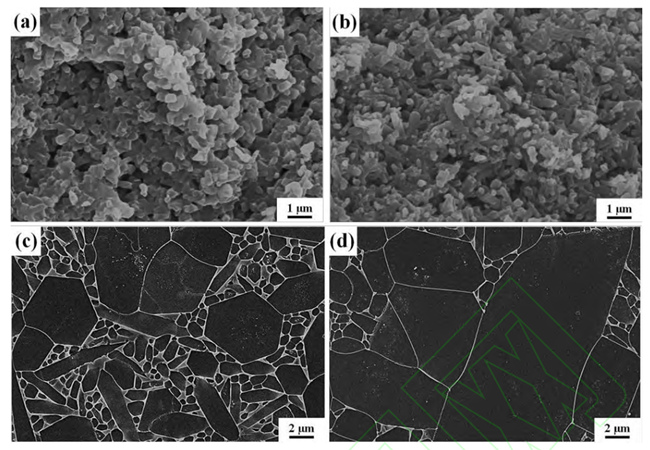
(a, c) Sample microstructure after nitriding without addition and (b, d) sample microstructure
after nitriding with buried powder containing C (a, b) and microstructure of silicon nitride after air
It is worth noting that the introduction of C needs to be controlled precisely in the sintering system of silicon nitride ceramics, the addition amount is too small, and the control effect of liquid phase is not good. Excessive addition will lead to residual SiC in the sample, which will adversely affect the density and electrical properties of silicon nitride ceramics. The results show that Si can also remove the surface oxide layer by silicothermal reduction reaction with SiO2. Unlike toner, which requires precise control of the amount of addition, excess Si is nitrided to Si3N4 in a nitrogen atmosphere, without the formation of harmful by-products.
The research of optimizing raw material powder of silicon nitride by carbothermal reduction and silicothermal reduction, and improving the performance of silicon nitride ceramics by means of liquid phase regulation provides a solution for the preparation of high thermal conductivity silicon nitride ceramics by using low-cost silicon nitride powders with high oxygen content.
격자 산소 함량이 낮은 질화규소 분말이 아직 획기적인 발전을 이루지 못한 배경에서 해당 산화물 소결 첨가제 대신 비산화물을 사용하고 액체를 조정함으로써 질화규소 세라믹의 열전도도를 향상시키는 경제적이고 효과적인 방법입니다. 위상 구성. 질화규소 원료 분말의 지속적인 최적화, 새로운 다기능 소결 첨가제의 지속적인 개발, 성형 및 소결 공정의 지속적인 개선으로 고강도, 고열 Si3N4 기판의 대규모 생산이 가능해졌습니다. 이는 전력반도체 소자 개발에 강력한 뒷받침이 될 것이다.





























